What Bonds Are Polar Covalent
There are two types of covalent bonds. Polar covalent bonds exist between two atoms with a difference between their electronegativity values in the range of 04 to 17.

Difference Between Chemistry Classroom Teaching Chemistry Chemistry Lessons
A The electrons in the covalent bond are equally shared by both hydrogen atoms.

What bonds are polar covalent. Both polar bonds and non-polar bonds are two types of covalent bonding between atoms. For example most carbon-based compounds are covalently bonded but can also be partially ionic. In such a bond there is a charge separation with one atom being slightly more positive and the other more negative ie the bond will produce a dipole moment.
To determine the polarity. Polar covalent bonds occur when there is a difference in electronegativity or electron affinity between covalently bonded atoms. Covalent bonds in which the sharing of the electron pair is unequal with the electrons spending more time around the more nonmetallic atom are called polar covalent bonds.
A covalent bond between atoms is formed when they share one or more pairs of electrons among each other. Here a high difference between electronegativity values means one atom having the higher electronegativity value attracts the electrons more than. This is a nonpolar covalent bond.
For example tetrachloro-methane carbon tetrachloride CCl 4 has polar CCl bonds but the tetrahedral arrangement of the four bonds about the central carbon atom causes the individual bond moments to cancel. For coordinate covalent bonds as for any other kind of bond it is impossible to distinguish among the electrons once the bond has formed. It is a bonding between atoms within a molecule and forms the strongest bonds anywhere.
This organic chemistry video tutorial explains how to identify a bond as an ionic bond polar covalent bond or a nonpolar covalent bond. In a b the polar covalent bonds are shown as lines. Covalent bonding is a form of chemical bonding between two non metallic atoms which is characterized by the sharing of pairs of electrons between atoms and other covalent bonds.
Covalent bonds are chemical bonds between two non-metal atoms. However a molecule may be polar or nonpolar depending on its geometry. A completely polar bond is more correctly called an ionic bond and occurs when the difference between electronegativities is large enough that one atom actually takes an electron from the other.
In covalent bonding the electrons are shared between the two atomic species involved instead of a complete giveaway or acceptance of electrons. Two atoms with equal electronegativity will make nonpolar covalent bonds such as HH. Explanation of Polar Covalent Bond Polar covalent bonds are usually formed between two nonmetal atoms having different electronegativities.
Net Dipole Moments Molecules as a whole are often polar from vector summation of individual bond polarities and loneindividual bond polarities and lone-pair contributionspair contributions Strongly polar substances soluble in polar solvents like water. A covalent bond in the bonding electrons are equally attracted to both atoms. Each diagram shows the unsymmetrical shape of the water molecule.
The bonding electrons in polar covalent bonds are not shared equally and a bond moment results. The terms polar and nonpolar are usually applied to covalent bonds that is bonds where the polarity is not complete. In non-polar covalent bonds electrons are equally shared by the two atoms participating in making the bond.
Covalent bonds are the most common and most important kind of bonding. A covalent bond that has an equal sharing of electrons part a of Figure PageIndex1 is called a nonpolar covalent bond. Ionic and covalent bonds are the two extremes of bonding.
Polar covalent is the intermediate type of bonding between the two extremes. The difference between ionic and covalent bonds is a bit ambiguous since the only truly nonpolar covalent bond occurs when two elements of the same atom bond with each other eg H 2 O 3Its probably better to think of chemical bonds as being more-covalent or more-polar along a continuum. In polar covalent bonds one atom has a stronger pull than the other atom and attracts electrons.
When both ionic and covalent bonding occurs in a compound the ionic portion is almost. What dictates which kind of bond will form. Electronegativity values of course.
Polar bonds are the dividing line between pure covalent bonding and pure ionic bondingPure covalent bonds nonpolar covalent bonds share electron pairs equally between atoms. Polar covalent bond A covalent bond in which a shared pair of electrons is held more closely by one of the atoms. However depending on the types of atoms involved the shared pair of electrons will not be residing at the centre.
Again polar covalent bonds tend to occur between non-metals. Lets go through each. Ionic Bond Covalent Bond James Bond so many bonds.
Ionic bond also known as electrovalent bond is a type of bond formed from the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions in a chemical compound. Covalent bonding occurs between two non-metallic atoms characterized by the sharing of electron pairs between the atoms and other covalent bonds with electronegativity difference is greater than 20. Some ionic bonds contain covalent characteristics and some covalent bonds are partially ionic.
Nonpolar substances are insoluble in water. Different ways of representing the polar sharing of electrons in a water molecule. Covalent bonds are also affected by the electronegativity of the connected atoms which determines the chemical polarity of the bond.
Remember how electrons carry a negative charge. In part c the polar covalent bonds are shown as electron dots shared by the oxygen and hydrogen atoms. Polar covalent bonds are made by two atoms with different electronegativities but the different should not be exceeding 17.
In polar covalent electron pair is pulled more by one atom compared to the other atom. Nonpolar covalent bonds form if this difference is lower than 04. Ionic Bonds Finally for atoms with the largest electronegativity differences such as metals bonding with nonmetals the bonding interaction is called ionic and the valence electrons are typically represented as being.
The polarity or lack thereof of a molecule greatly affects how it interacts with other molecules. Figure PageIndex1 Polar versus Nonpolar Covalent Bonds. An unequal relationship creates a polar covalent bond such as with HCl.
Technically nonpolar bonding only occurs when the atoms are identical to each other eg H 2 gas but chemists consider any bond between atoms with a difference in electronegativity less than 04 to be a. In the case of covalent bond formation polyatomic ions are formed. The donor atom provides both electrons to a coordinate covalent bond and the acceptor atom accepts an electron pair for sharing in a coordinate covalent bond.
The covalent bond formed between two atoms in molecules whose electronegative difference exists is known as a polar covalent bond. In a polar covalent bond shown in Figure 1 the electrons are unequally shared by the atoms and are attracted more to one nucleus than the otherBecause of the unequal distribution of electrons between the atoms of different elements a slightly positive δ or slightly negative δ charge develops.

Polar Bond Easy Science Covalent Bonding Chemistry Easy Science

Polar Vs Nonpolar Covalent Bonding Medical Student Study Science Chemistry

Triple Covalent Bond Covalent Bonding Bond Easy Science

Types Of Chemical Bonds Chemistry Lesson Package Chemistry Lessons Chemical Bond Science Lessons High School

Water Has Both A Hydrogen Bond And A Polar Covalent Bond Hydrogen Bond Chemistry Classroom Covalent Bonding

Difference Between Polar Covalent Bond And Non Polar Covalent Bond Covalent Bonding 11th Chemistry Chemistry

Polar Nonpolar Covalent Bonds Ch 6 Youtubea Little Too Detailed Though Covalent Bonding Chemistry Classroom Chemistry Lessons

Polar Covalent Bonds Covalent Bonding Teaching Chemistry Chemistry Help

Polar And Nonpolar Molecules Covalent Bonding Chemistry Lessons Molecules
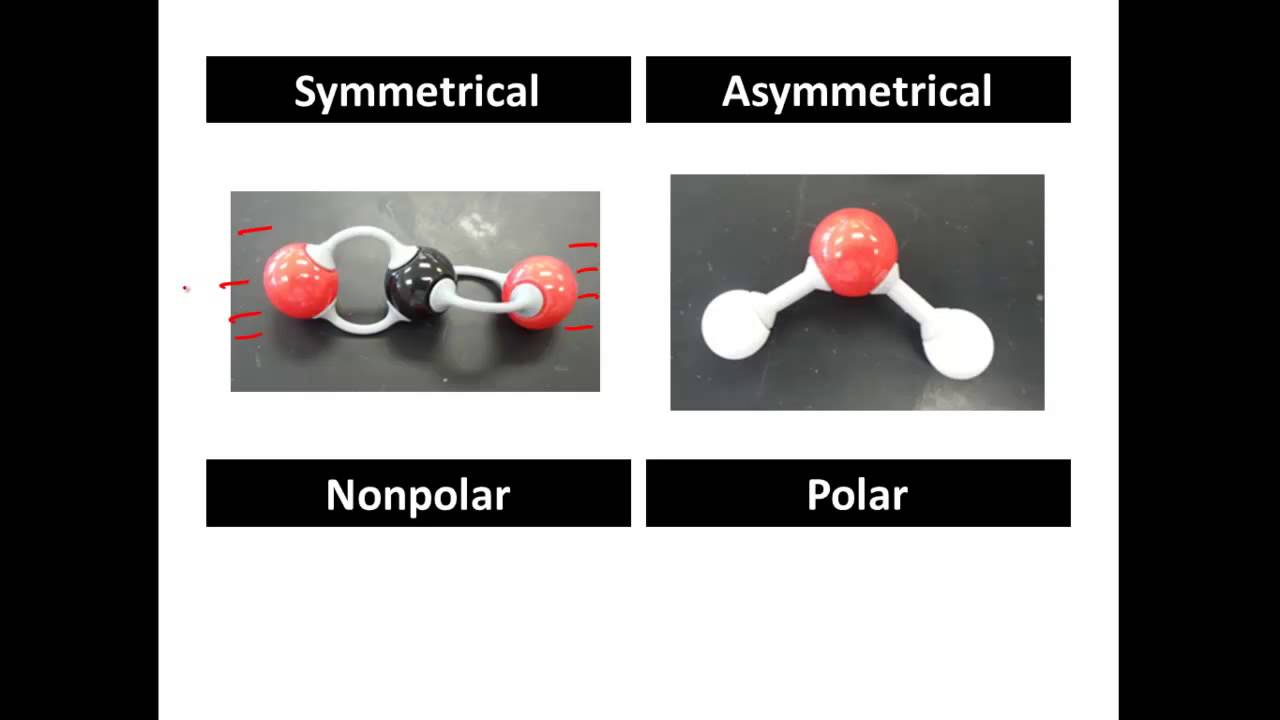
Polar And Non Polar Covalent Molecules Polar Vs Nonpolar Youtube Playlist Science Chemistry Molecules Chemistry

Definition And Examples Of A Polar Bond In Chemistry Covalent Bonding Chemical Bond Chemistry

Details Here Https Dantuckerautos Com Fresh Protons In Carbon Covalent Bonding Polar Graphics Design Ideas

Infographic Defining Bonds As Electronegativity Differences En Intermolecular Force Chemistry Linus Pauling

About The Mcat Mcat Chemistry Chemical Reactions Ciencias Quimica Quimica Cine En Casa

Difference Between Polar And Nonpolar Molecules Definition Formation Properties Examples Covalent Bonding Study Chemistry Chemical Bond

Polar Covalent Nonpolar Covalent Ionic Bonds Ionic Bonding Physics Lessons Science Chemistry

Bond Polarity Organic Chemistry Study Chemistry Lessons Chemistry Classroom

Polar Covalent Bonds Covalent Bonding 8th Grade Science Biology

Science Coverage Is No2 Polar Or Nonpolar Electron Affinity Covalent Bonding Molecular Geometry